...
The redesign also fires event signals into a passive message sniffer subsystem to simplify the debugging process. The default message sniffer subsystem's GUI component can be accessed using the "Message Log" link that is visible when debugging mode is turned on for a project.
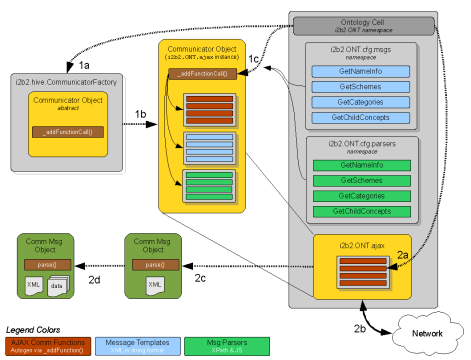
Overview of Communicator Subsystem
| Anchor |
|---|
DDE_LINK | DDE_LINK | The general initialization of a communicator instance is as follows:
...
You may optionally define a namespace to hold any functions you plan on using to process the returned XML document into a more easily worked with native-JavaScript format. Best practice is to call these namespaces msgs and parsers respectively and to add them to your cell / plug-in's cfg namespace.
| Anchor |
|---|
| _GoBack | _GoBack | // create the communicator Object
i2b2Objecti2b2.ONT.ajax = i2b2.hive.communicatorFactory ("ONT");
// create namespaces to store the communicator's msg templates and parsers
i2b2.ONT.cfg.msgs = {};
i2b2.ONT.cfg.parsers = {};
...
Now the individual XML message templates need to be created. These templates are simply strings saved into the msgs namespace. Best practice is to save them using a name that is the same as the i2b2 Hive RPC call.
i2b2.ONT.cfg.msgs.GetSchemes =
'<?xml version="1.0" encouding="UTF-8"
standalone="yes"?>\n'
'<ns3:request xmlns:ns3="http://www.i2b2.org/xsd/hive/mghs/1.1."
xmlns xmlns:ns4="http://www.i2b2.org/xsd/cell/ont/1.1/"
xmlns xmlns:ns2="http://www.i2b2.org/xsd/hive/plugin/">\n'
' <message <message_header>\n'
' {{{proxy_info}}}\n'
' <i2b2_version_compatible>1.1</i2b2_version_compatible>\n'
' <hl7_version_compatible>2.4</hl7_version_compatible>\n'
' <receiving_facility>\n'
' <facility <facility_name>i2b2 Hive</facility_name>\n'
' </receiving_facility>\n'
' <datetime_of_message>{header_msg_datetime}</datetime_of_message>\n'
' <security>\n'
' <domain>{sec_domain}</domain>\n'
' <username>{sec_user}</username>\n'
' {sec_pass_node}\n'
' </security>\n'
' <message <message_control_id>\n'
' <message_num>{header_msg_id}</message_num>\n'
' <instance_num>0</instance_num>\n'
' < </message_control_id>\n'
' <processing <processing_id>\n'
' <processing_id>P</processing_id>\n'
' <processing_mode>I</processing_mode>\n'
' < </processing_id>\n'
' <accept <accept_acknowledgement_type>AL</accept_acknowledgement_type>\n'
' <application <application_acknowledgement_type>AL</application_acknowledgement_type>\n'
' <country <country_code>US</country_code>\n'
' <project <project_id>{sec_project}</project_id>\n'
' < </message_header>\n'
' <request <request_header>\n'
' <result <result_waittime_ms>{result_wait_time}000</result_waittime_ms>\n'
' < </request_header>\n'
' <message <message_body>\n'
' <ns4 <ns4:get_schemes type="default"/>\n'
' < </message_body>\n'
'</ns3:request>'; |
Placeholder tags starting, and ending, with three curly brackets ( "{" and "}" ) are contained throughout this message string. Between the tag's curly brackets is its non-space containing name used to identify the tag. These tags are replaced with values passed in the call parameters when the communication method is invoked.
...
You may create a message parser to simplify your own code and to allow other developers to more easily integrate with your standardized cell communicator. When your parser is invoked its this variable references the standard Communicator Results Object ("CRO") that is returned by the communicator subsystem.
i2b2.ONT.cfg.parsers.GetSchemes = function(){
' ' ' ' ' if (!this.error){
<ac:structured-macro ac:name="unmigrated-wiki-markup" ac:schema-version="1" ac:macro-id="a68c826bd6cdfe81-f7989dc5-48554c15-9dbea5d7-54451e62ee0f72919c76316b"><ac:plain-text-body><![CDATA[
i2b2.ONT.cfg.parsers.GetSchemes = function(){ if (!this.error) { this. ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' this.model = []; ]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro>
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' // extract records from XML msg
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' var c = this.refXML.getElementsByTagName('concept');
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' for (var i=0; i < 1 * c.length; i++) {
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' var o = new Object;
<ac:structured-macro ac:name="unmigrated-wiki-markup" ac:schema-version="1" ac:macro-id="8fe6ffbc-3d3e-41c6-9314-4e2642781ea9"><ac:plain-text-body><![CDATA[
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' o.xmlOrig = c[i]; ]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro>
<ac:structured-macro ac:name="unmigrated-wiki-markup" ac:schema-version="1" ac:macro-id="f3e6d812-37fa-40db-a3c7-5e80f7a7f9a5"><ac:plain-text-body><![CDATA[
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' o.level = i2b2.h.getXNodeVal(c[i],'level'); ]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro>
<ac:structured-macro ac:name="unmigrated-wiki-markup" ac:schema-version="1" ac:macro-id="6dcb1a7f-6232-4495-a6ba-b437f55ea616"><ac:plain-text-body><![CDATA[
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' o.key = i2b2.h.getXNodeVal(c[i],'key');]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro>
<ac:structured-macro ac:name="unmigrated-wiki-markup" ac:schema-version="1" ac:macro-id="9f62274d-bb3f-4e5d-ac3d-9117348dbd14"><ac:plain-text-body><![CDATA[
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' o.name = i2b2.h.getXNodeVal(c[i],'name'); ]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro>
<ac:structured-macro ac:name="unmigrated-wiki-markup" ac:schema-version="1" ac:macro-id="6684ac88-393c-4a8a-8ea8-2e19f33c4e2e"><ac:plain-text-body><![CDATA[
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' o.total_num = i2b2.h.getXNodeVal(c[i],'totalnum'); ]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro>
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' // save extracted info
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' this.model.push(o);
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' }
' ' ' ' ' } else {
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' this.model = false;
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' console.error(| Wiki Markup |
|---|
"\[GetSchemes\] Could not parse() data\!" |
);
' ' ' ' ' }
' ' ' ' ' return this;
}; | ]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro> |
| Note |
|---|
|
Very specific behavior is expected from your parser function! Your parser is expected to create an array called this.model containing a list of values or JavaScript objects representing data from the XML message. If an error occurs, your parser is expected to set this.model = false. Your parser routine must always return the reference to its this variable |
...
...
Creating Communication Methods
The generic communicator object returned by calling the i2b2.hive.communicatorFactory() function consist of several private use functions and data structures. The _addFunctionCall() function is to be used by your initialization routine to create communicator methods that are to be called by non-framework code, such as the code in your cell / plug-in. To continue with this section's example and create the ONT cell's GetSchemes communication method the following code is executed:
i2b2.ONT.ajax._addFunctionCall("GetSchemes",
' ' ' ' ' "{URL}getSchemes",
' ' ' ' ' i2b2.ONT.cfg.msgs.GetSchemes,
' ' ' ' ' null,
' ' ' ' ' i2b2.ONT.cfg.parsers.GetSchemes); |
...
<div id="ExampTabs-mainDiv">
<cell_datas>
' ' ' ' ' <cell_data id="ONT">
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' <name>Ontology Cell</name>
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' <url>http://webservices.i2b2.org/i2b2/rest/OntologyService/</url>
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' <project_path>/</project_path>
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' <method>REST</method>
' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' <can_override>true</can_override>
' ' ' ' ' </cell_data>
</cell_datas> |
The required third parameter is a reference to the XML message template that is to be sent to the i2b2 hive back-end when the i2b2.ONT.ajax.GetSchemes() communicator method is called. The message always has its special tags replaced with the values passed to the communicator method.
The optional fourth parameter is an array containing the names of tags used in the XML message template that should NOT be escaped. For example, if a specific message tag is supposed to be interpreted as additional XML elements you will want to make sure that it is not escaped automatically by the communicator subsystem. If you are not using this parameter you can omit it from the function parameter list unless you are passing a 5th parameter, in which case you should set the 4th parameter to be null. An example of passing values using the optional 4th parameter is as follows:
i2b2.CRC.ajax._addFunctionCall("runQueryInstance_fromQueryDefinition",
' ' ' ' ' "{URL}request",
' ' ' ' ' i2b2.CRC.cfg.msgs.runQueryInstance_fromQueryDefinition,
' ' ' ' ' "psm_result_output""psm_query_definition""shrine_topic"]); |
...
| Note |
|---|
|
To ensure stability of your Web Client deployment, do not change the default message parser of any cell or plug-in this is not owned in-house.
If a cell / plug-in does not extract all the information you need from its XML message you can copy the code to your own namespace, modify it, and pass its references as a parameter to the Communication Data Objects parse() function. Doing this will override usage of the default message parser in a way that will allow code updates without stability issues related to version mismatches or applying custom patches. |
...
...
Using the Communicator
...
Standard Communication Method Parameters
All communication methods created using the _addFunctionCall() function of a communicator instance operate in exactly the same way and consume the same parameters. Below is a list of all parameters of a standard communications method:
Parameter | Required | Description |
originName | N | String that is used to identify and group all messages using the message sniffer subsystem. |
tagValues | N | A JavaScript object using tagname / value pairs. An example would be:
{ ont_synonym_records: "N",
ont_hidden_records: "N",
ont_search_strategy: "contains",
ont_search_string: "asthma" } |
scopedCallback | Y | A scopedCallback object or regular function used to enable asynchronous AJAX calls.
If omitted, synchronous calls are used instead. |
transportOptions | Y | Transport options passed directly to Prototype's AJAX object.
See http://api.prototypejs.org/ajax/ajax/request/ for more information. |
...
...
Synchronous Call Example
A code example showing how to perform a synchronous request on a standard communicator method:
// create the object containing tag/value pairs to be used by the XML msg template
var tagValues = { ont_synonym_records" "N",
ont_hidden_records" "N",
ont_search_strategory" "contains",
ont_search_string" "asthma",
};
// use synchronous call to request results from the i2b2 Hive back-end
var results_cdo = i2b2.ONT.ajax.GetNameInfo ("originated by test", tagValues);
// dump the Communication Data Object variable (Firefox w/Firebug only)
console.dir (results_cdo);
// dump the sent xml (Firefox w/Firebug only)
console.debug (results_cdo.msgRequest);
// dump the returned xml (Firefox w/Firebug only)
console.debug (results_cdo.msgResponse); |
...
...
Asynchronous Call Example
Here is a code example showing how to perform an asynchronous request on a standard communicator method:
...
// create scoped-callback object (attaches execution scope to complexAsynchCallback)
var scopedCB = new i2b2_scopedCallback () ;
scopedCB.scope = window.console;
scopedCB.callback =complexAsyncCallback; |
...
...
Communication Data Object ("CDO")
All standardized communication method calls, regardless of synchronous or asynchronous execution, return a standard results object known as a Communication Data Object which contains details of the messages passed back and forth between the web client and the i2b2 Hive back-end.
Attribute Name | Type | Description |
Result.error | Boolean | Information used by to Web Client's proxy server |
Result.msgRequest | String | The message that was sent to the proxy server (and thus the i2b2 Hive web service) |
Result.msgResponse | String | Code of current project |
Result.msgUrl | String | The URL used to access the i2b2 Hive web service call. |
Result.msgUrlProxy | String | The URL of the proxy that the web client sent the message to. |
Result.refXML | XMLDOM | A reference to a XMLDOM object containing the response message. |
Result.parse() | Function | A function called by a developer's code to automatically parse the XMLDOM and save the results in Result.model attribute. |
Result.model | Null or Array | This attribute is created after calling the parse() function. |
...
...
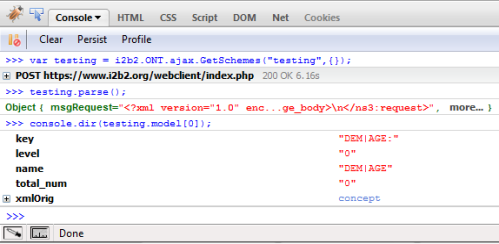
Message Parser Examples
The following code shows how to use the default parser function on a returned Communication Data Object:
// executing from Firebug console window, run synchronous GetSchemes webservice
// call with a debug title of "testing" and empty template vars denoted with {}
var testing = i2b2.ONT.ajax.GetSchemes ("test msg", {}) ;
console.dir (testing) ;
// run the default GetSchemes parser and populate the "model" attribute of the CDO
testing.parse () ;
// dump the first record from the "model" attribute of the CDO
console.dir (testing.model[0]) ; |
The results will be output as so: